Automation Workshop can automate IT and business tasks without writing a line of code. Let's see how we can ensure file integrity when moving them to an archive.
Overview
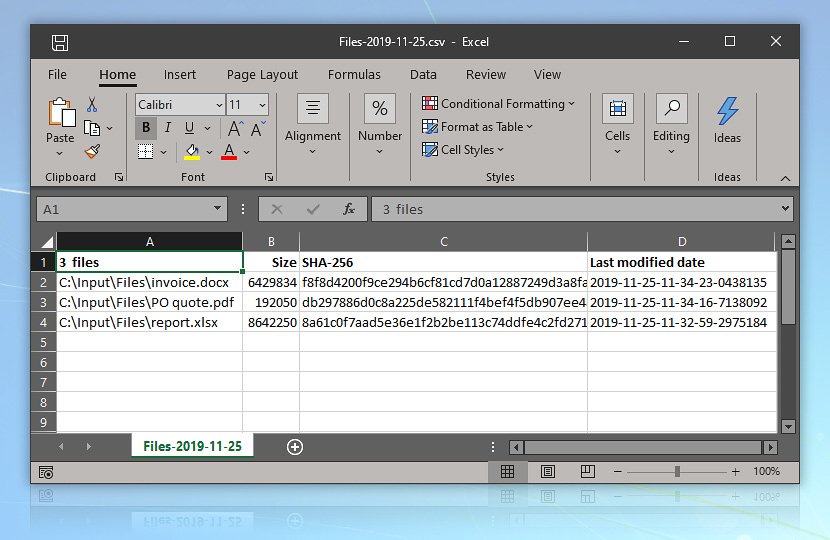
Files from multiple sources are copied to the C:\Input\Files folder. At regular intervals, 4 times a day, Automation Workshop moves folder contents to a unique date-based backup folder. Before moving files to backup, their names, sizes, checksums and last modified dates are recorded in a .csv text file to provide a means for verifying file integrity later. We will collect data on files before moving them to the backup folder.
Solution
Set up the Task Scheduler trigger that will run the Task 4 times a day (once every 6 hours). The Task will list all files in the C:\Input\Files folder. A subfolder with date and time in its name will be created in C:\Backup folder.
If there are no files, a corresponding record will be written in the no files.txt file in the C:\Backup\Date folder. If there are one or more files, for each of them a series of Actions will be performed:
- Get File Information Action will retrieve the file name and file size.
- Compute File Hash Action will calculate file checksum.
- Get File Date & Time Action will read the last modified date and time attribute.
- Write to File Action will store data on each file in a text file in the
C:\Backup\Datefolder. - Move File Action will move the processed file to the
C:\Backup\Datefolder.
Schedule
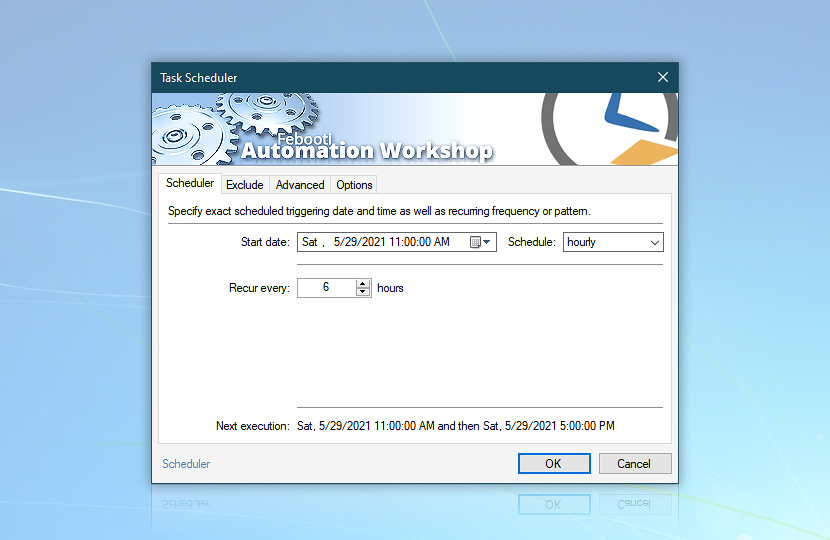
First, let's set up a Task Scheduler trigger that will regularly launch the Task with 6 hour intervals. Specify a start date and time and an hourly schedule with a 6-hour recurrence period.
Actions
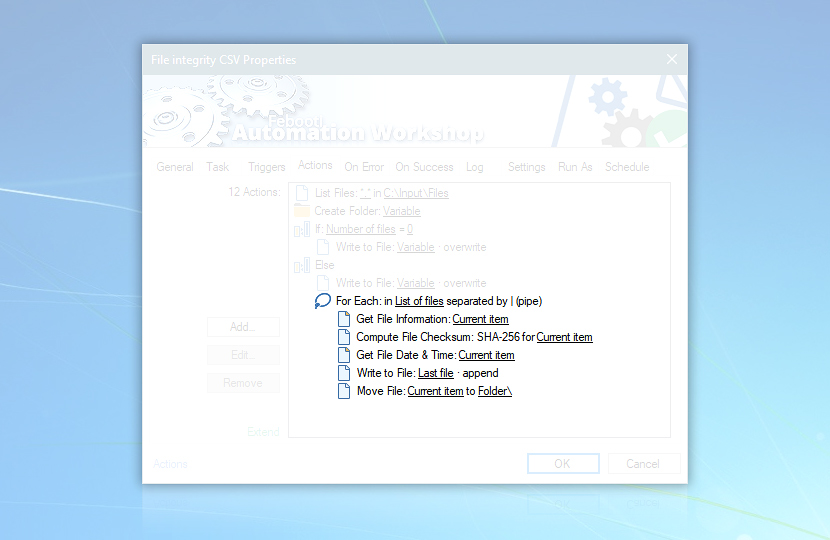
Let's set up Actions for the Task. This is how the Action tab of a fully configured Task looks:
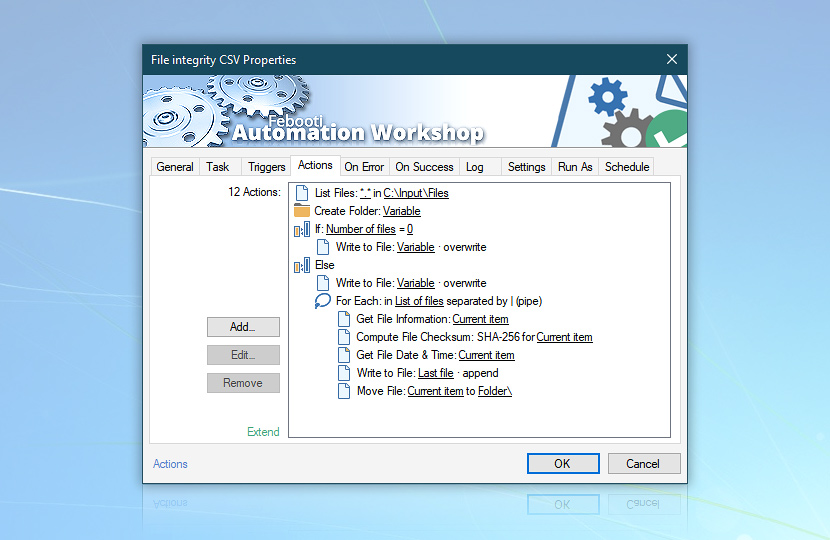
Information among Actions is passed by the Variable Wizard (see underlined elements in the Action tab and green, bold text in parameter fields of Actions).
Notice the indent of Write to File and For Each Actions relative to the If and Else Actions. It means that the first Write to File Action will be performed only if the number of files in the folder is 0, while the second Write to File Action will be performed if the number of files in the folder is not 0.
Likewise, the indentation in front of a group of Actions (relative to the For Each Action) indicates that they are subordinate to the For Each action. The For Each Action runs its subordinate Actions for every file it processes (as it processes files retrieved by the List Files Action and stored in the List of files variable).
List files
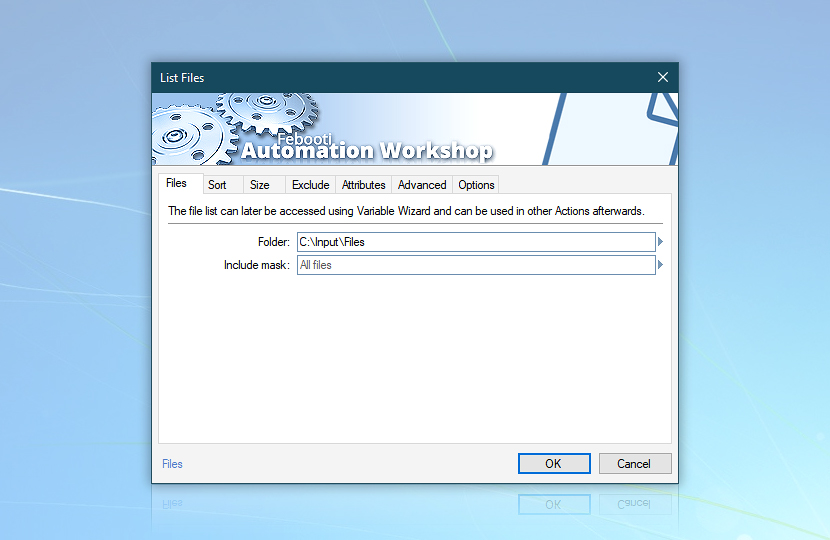
Let's use the List Files Action to retrieve the list of all files currently in the C:\Input\Files folder.
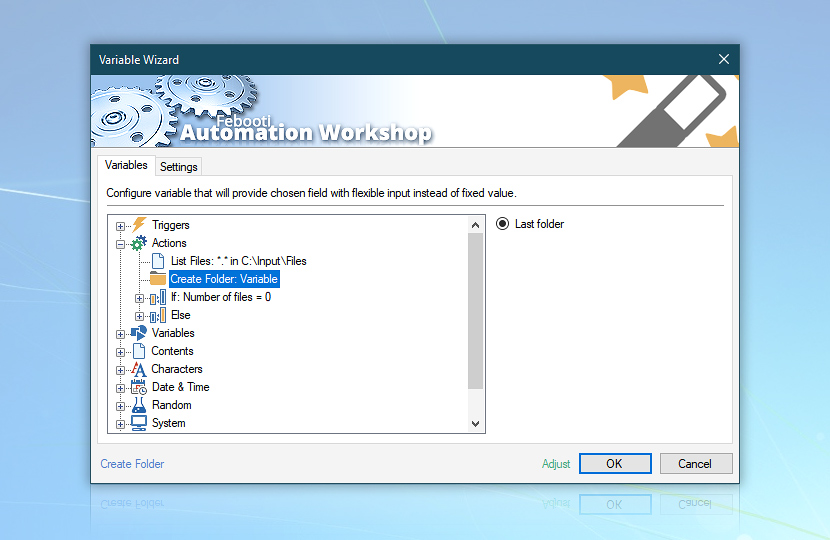
Create folder
Let's use the Create Folder Action to create a subfolder in the C:\Backup folder with the current date and time in its name. We will store both reports and files here. Alternatively, employ the Ensure Folder Action, which seamlessly ensures that the specified folder exists, accommodating both scenarios where the folder already exists or does not.
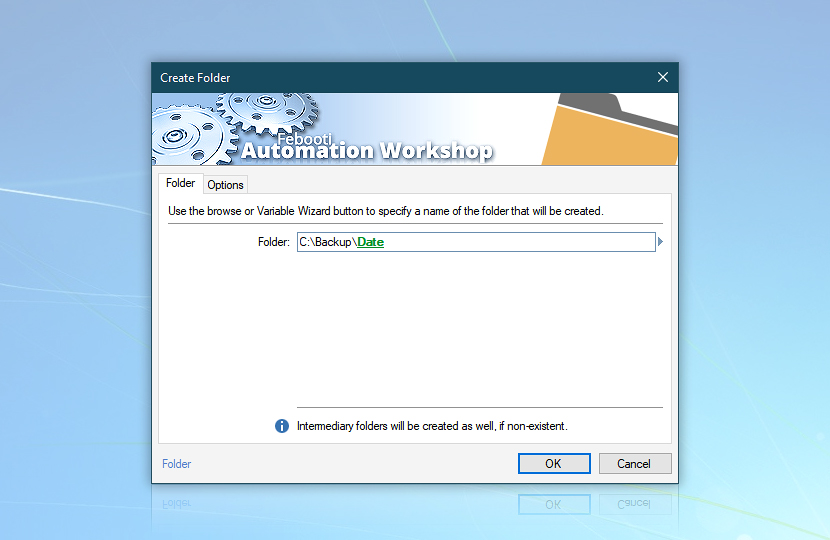
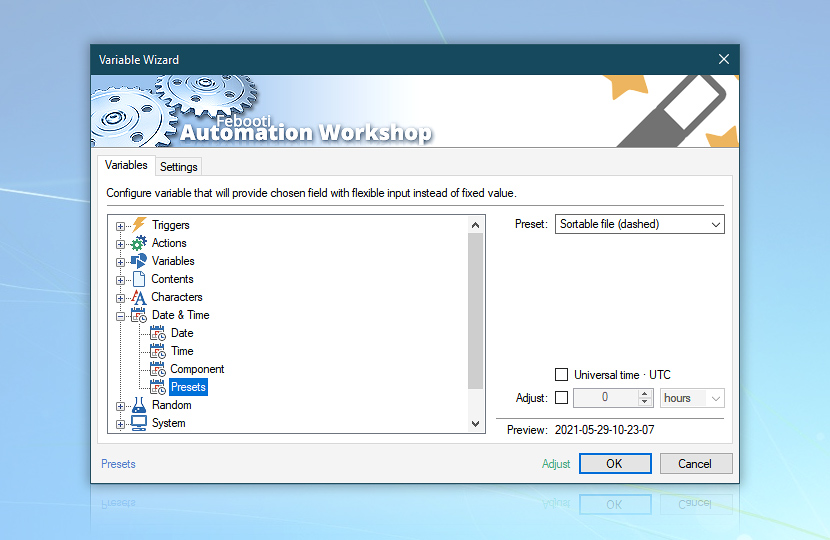
Insert variable after C:\Backup\ text and choose Preset: Sortable file (dashed).
If
Now we will verify whether there are currently any files in the C:\Input\Files folder. If there are none, we will note it in the no files.txt file. Else (if there are some), we will process them one by one and store information in the Files-Date.csv file.
Set up the If Action so that it checks if the Number of files returned by the List Files Action is equal to 0.
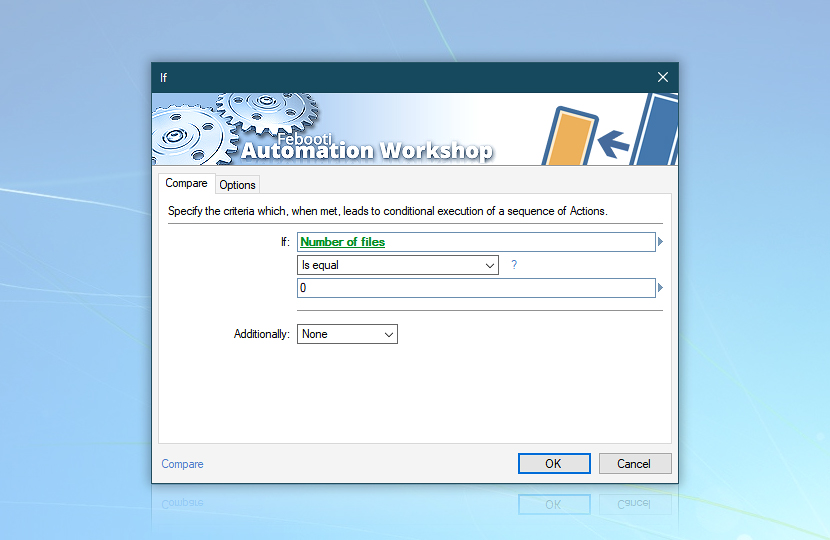
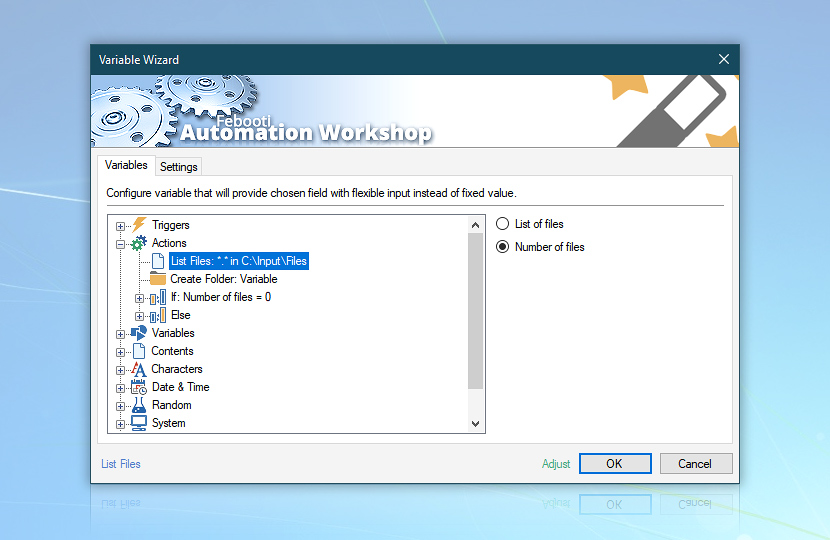
Use Variable Wizard to retrieve the Number of files variable from the List Files Action.
No files?
Add the Write to File Action that will write the No files… text in the no files.txt file when there are 0 files listed.
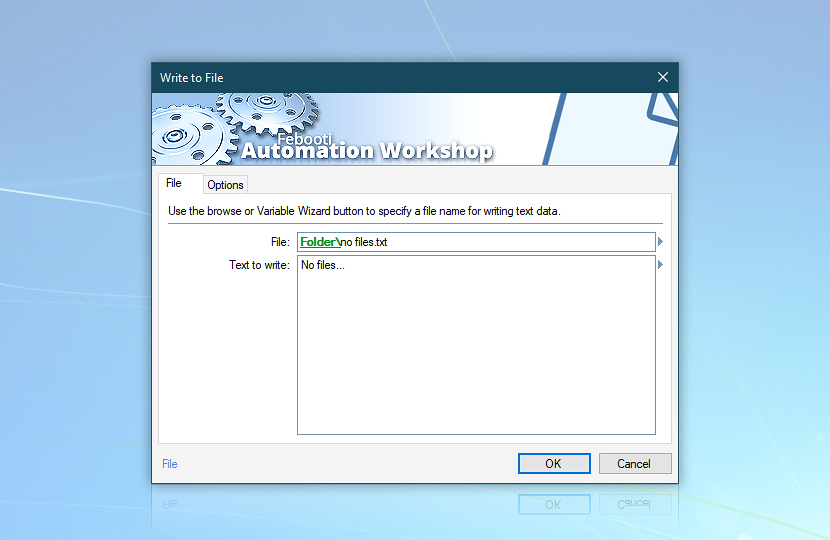
Let's take the destination path (i.e., Last folder) from the Create Folder Action by using Variable Wizard.
Else
Add the Else Action to denote the alternative conditional branch. As specified in the If part, this branch will only be performed when the List Files Action returns more than 0 files. See that it has the same indentation level as the If Action (i.e., no indent or the leftmost side of the list). Add a subordinate Write to File Action.
To ensure full compatibility with Microsoft Excel, uncheck the Save file using Unicode encoding checkbox in the options tab.
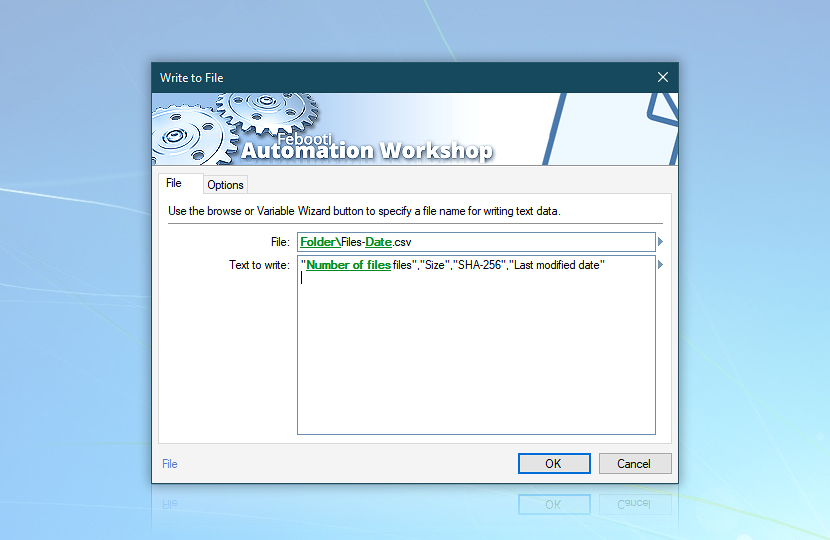
The Text to write field is organized in comma-separated columns that correspond with the order of the following Actions which will provide data for each of them. Note the 3 variables in the configuration of the Write to File Action:
1) The Last folder value is taken from the Create Folder Action to specify that the report file will be created in the C:\Backup\Date folder.
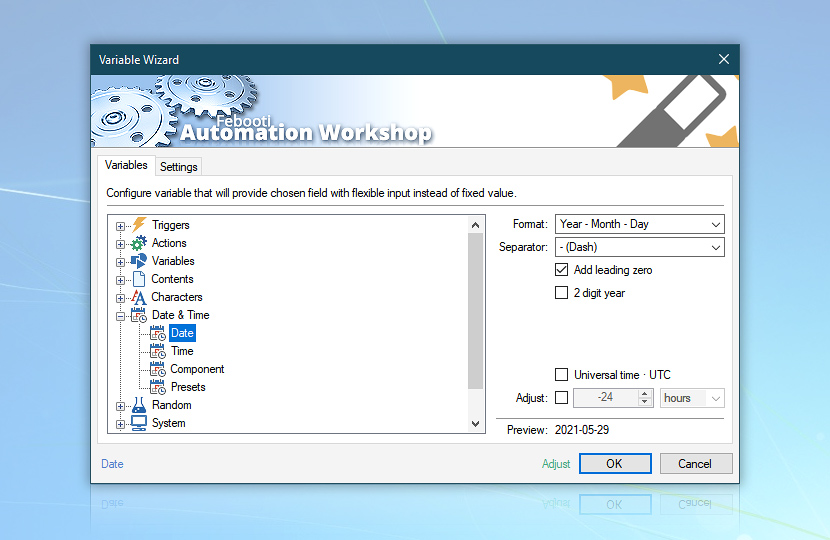
2) The Date in Report-Date.csv is taken from the Date variable set to the Year / Month / Day format with a leading zero added (so that chronological order matches the alphabetical one).
3) The Number of files variable is taken from the List Files Action.

When all 3 variables are combined in the Write to File Action, it creates a unique CSV file with the current date in its name in the previously created folder and writes a comma-separated header row that defines its structure.

For Each…
Now let's fill this CSV file with data about each listed file. We will process each file one by one, read its data, and store it in the created CSV file.
When collecting information about listed files, we will run the same set of Actions for each file. The For Each Action will perform the cycle by launching subordinate Actions one by one. Add the For Each Action and use the Variable Wizard to load the List of files from the List Files Action.
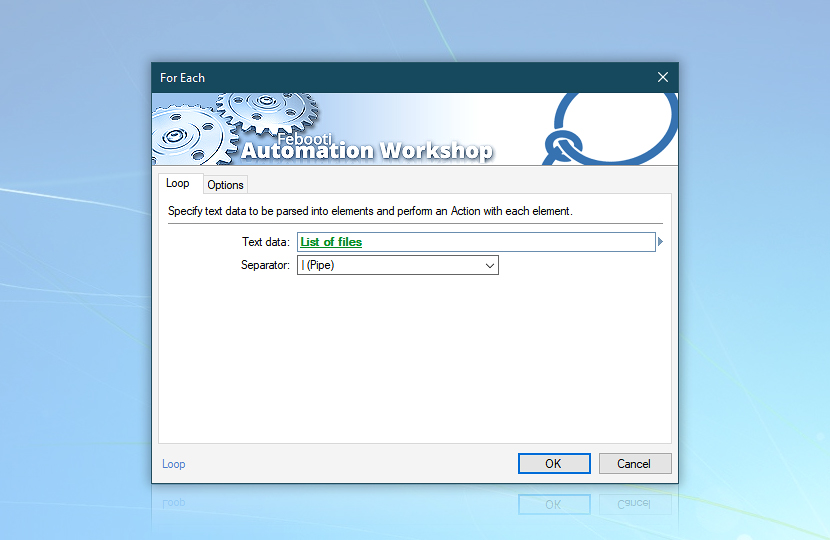
The For Each Action will split a file list into individual files and run a set of subordinate Actions for every file.
Now, let's collect relevant data to fill the CSV file. We will use 3 Actions:
- Get File Information Action to get the name of the current file (the name of file used in current step of the cycle).
- Compute File Checksum Action to calculate SHA-256 checksum for current file.
- Get File Date & Time Action to retrieve the modified date of current file.
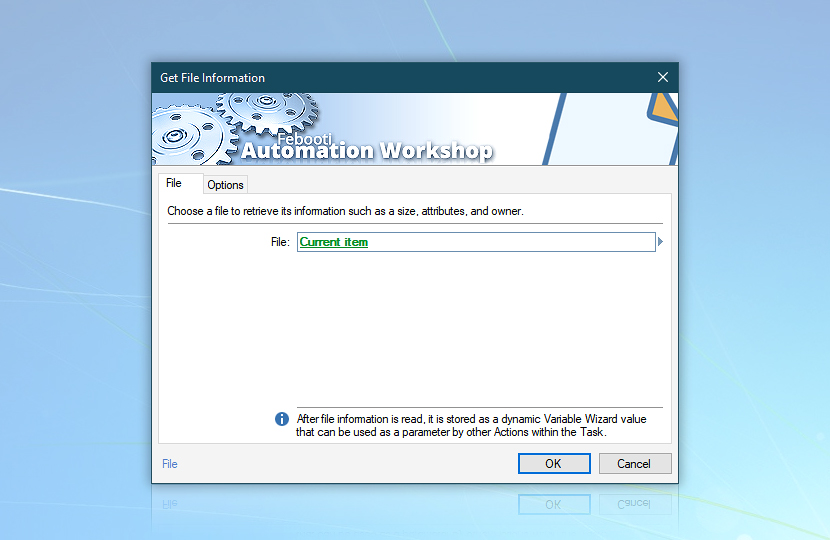
Use the Variable Wizard to refer to the Current item in the For Each Action to get information on a file processed in the current step of the cycle.
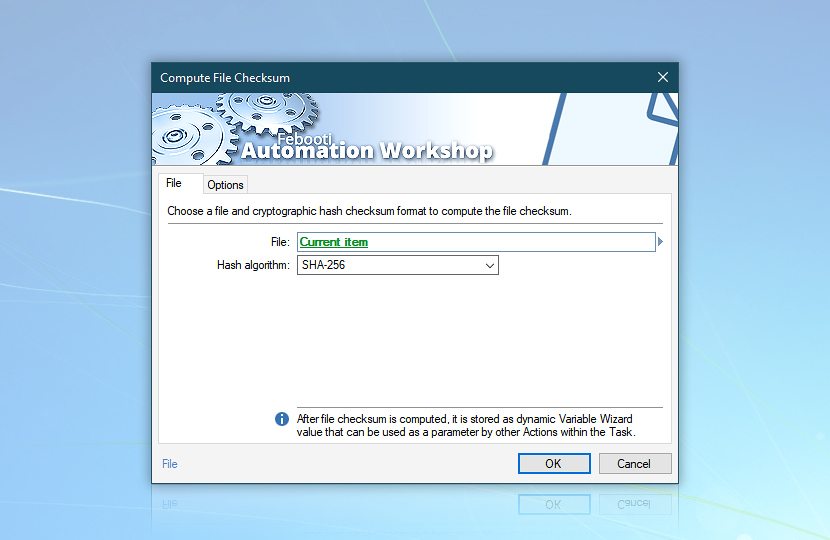
Use the Variable Wizard to refer to the Current item in the Compute File Checksum Action to get a hash cryptographic checksum for a file processed in the current step of the cycle.
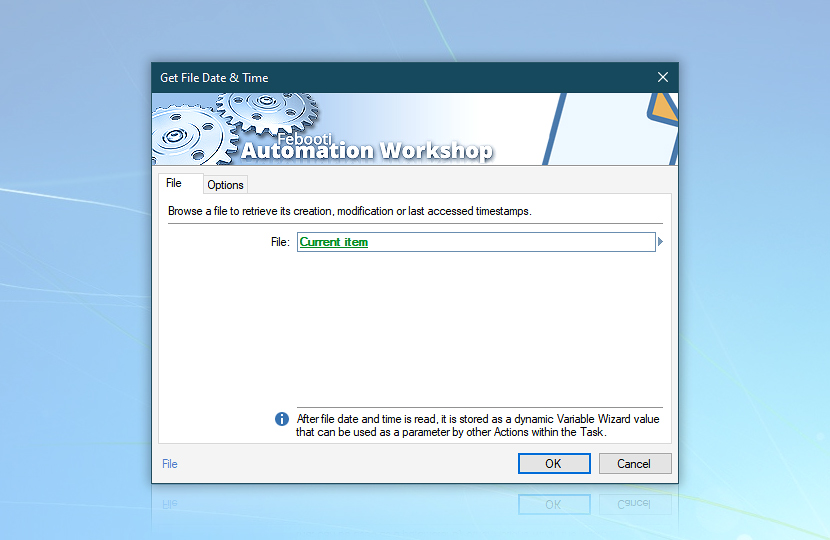
Use the Variable Wizard to refer to the Current item in the Get File Date & Time Action to get information when the file processed in the current step of the cycle was last modified.
Once all three Actions have collected the necessary data on the current file, let's use the Write to File Action to write it in the CSV file.
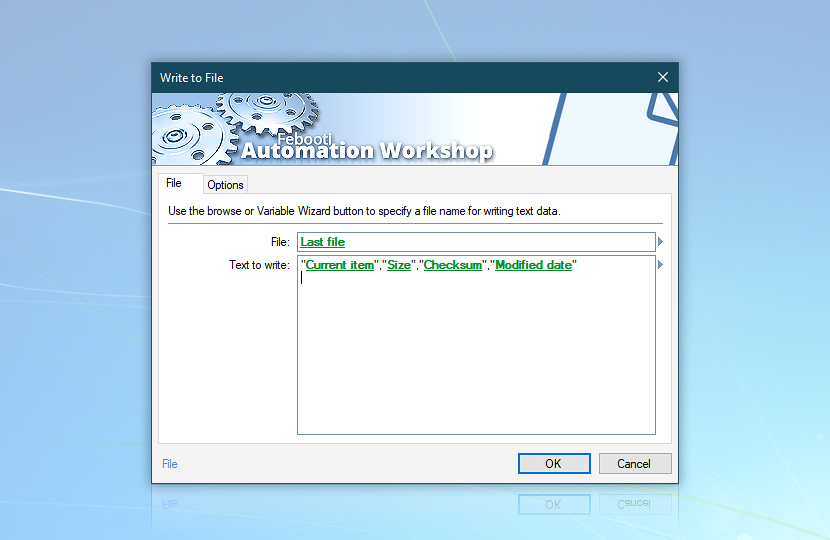
Using Variable Wizard we will complete a few steps to collect all necessary data together.
- To indicate the CSV file, specify the Last file variable from the previous Write to File Action. Note that append mode should be used rather than overwrite so that each step adds on rather than deletes the previous one.
- To indicate the content to be written in the CSV file, use the Current item from the For Each Action, the Size from the Get File Information Action, the Checksum from the Compute File Checksum Action, and the Modified date from the Get File Date & Time Action. Each variable should be placed in quotes and comma-separated to match the header structure (to guarantee CSV integrity for flawless compatibility with Microsoft Excel).
As a result, the information will be collected for each file in the For Each loop (that takes the file list from the List Files Action) and stored in a unique CSV file.
Move to backup
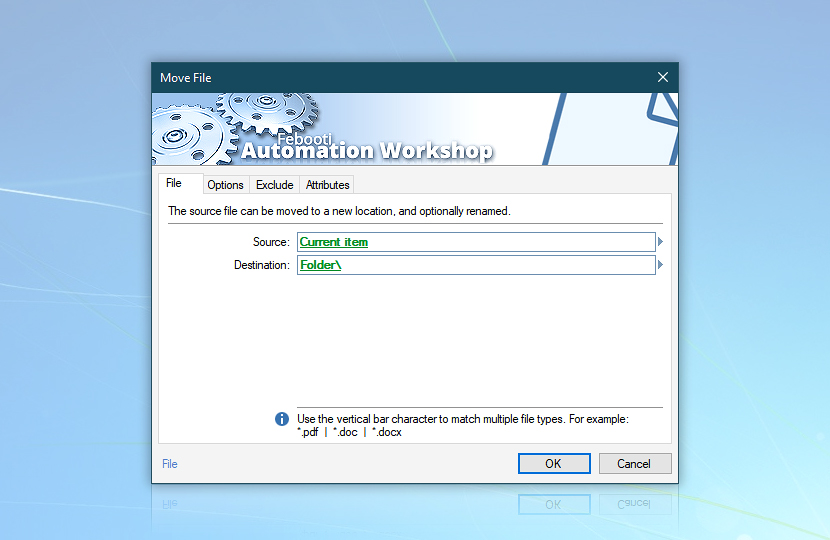
Finally, let's move the processed file itself to the Backup folder (where we stored the CSV file).
Let's create a Move File Action and use the Variable Wizard for both Source and Destination parameters—for the source, use the Current item from the For Each Action; for the destination, refer to the Last folder in the Create Folder Action.
Conclusion
The resulting Task consists of 12 distinct Actions that are performed once every 6 hours. The Actions analyze whether there are files in C:\Input\Files folder and reports every run in a unique date-based backup folder.

When files are found, various data is collected and stored in a CSV file to ensure backup integrity before moving files to the backup folder.
We are here to help…
If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact our support team.
