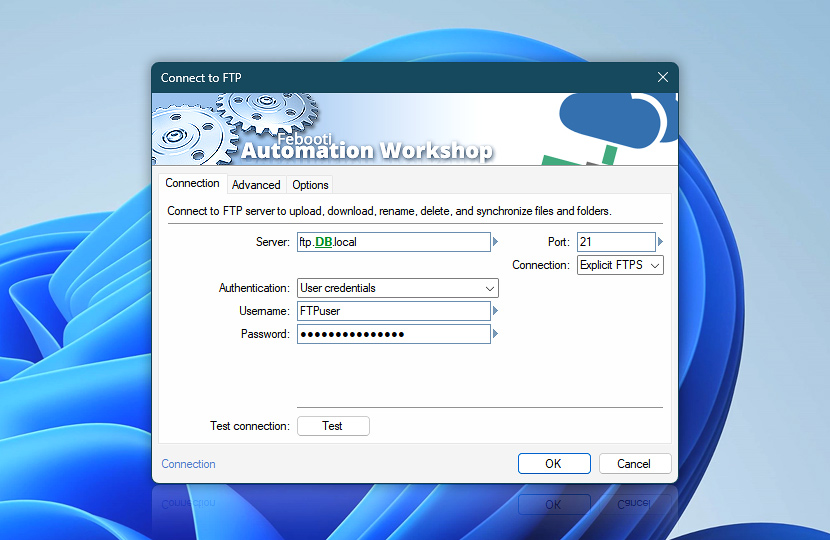
Connect to an FTP (File Transfer Protocol) server to monitor for file changes or perform a variety of operations with remote files and directories.
| Connection | Details |
|---|---|
| Server | FTP server name or IP address. |
| Port | The FTP server port to connect to. Usually, FTP and explicit FTPS use port 21, while implicit FTPS uses port 990. |
| Connection | The Connect to FTP Action supports both non-encrypted (plain) and encrypted (FTP-SSL) connections.
|
| Authentication | Depending on the server settings, use user credentials or user credentials with a client certificate.
The Anonymous standard option is the most popular. However, there are numerous FTP server implementations that only accept the simple or open standard. Both fields are editable to allow even more customization. |
| Username | Specify the username. |
| Password | Specify the password. |
| Client certificate path | For client certificate authentication, provide a client certificate file. Supported formats include Personal Information Exchange (.pfx or .p12) and Base64 encoded X.509 (.pem or .key).A private key and certificate can be provided in two separate files. The files must have the same name with different extensions. Automation Workshop looks for .crt or .cer files if the provided file contains only a private key section. For example:
|
| Certificate passphrase | For client certificate authentication, provide the certificate passphrase. |
| Mask password | |
| Browse | |
| Variable Wizard |
Interconnect
- Connect to FTP integration and auditing—Variables (dynamic data) and Events (recorded activity). Retrieve the FTP or FTPS server name (address) and its fingerprint. Comprehensive log records are kept, covering any issues faced during the connection.
Notes
- Some FTP servers require a Windows domain username, for example:
Domain\username. - For some FTP servers, it may be necessary to change stateful FTP firewall settings.
Need assistance?
If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact our support team.